Your car releases toxins, but thanks to the catalytic converters that clean out the toxins, your car does not pollute the environment. But do you know the elements which clean the toxins out of the exhaust fumes?
One of the important elements is the rhodium which works with other elements such as palladium to clean the toxins before the fumes are released to the environment.
Unfortunately, rhodium is a rare metal and is worth more than gold; so how much rhodium is in a catalytic converter? Read on to learn more about the rhodium used in catalytic converters.
Contents
So, How Much Rhodium Is in Catalytic Converter?
The answer to this question depends on some factors, especially on the car’s make and model, and its engine. One vehicle with the same engine could have different converters for different countries.
The average quantity of rhodium in a catalytic converter is about 1-2 grams, and the average weight of a catalytic converter is about 1.2 kg or 2.2 pounds.
Rhodium has a very high cost, about $290 per gram, but the price would depend on the metal quality, but you can easily fetch this from recycling the old converter.
Can Rhodium Coming From A Used Catalytic Converter Lose Its Properties?
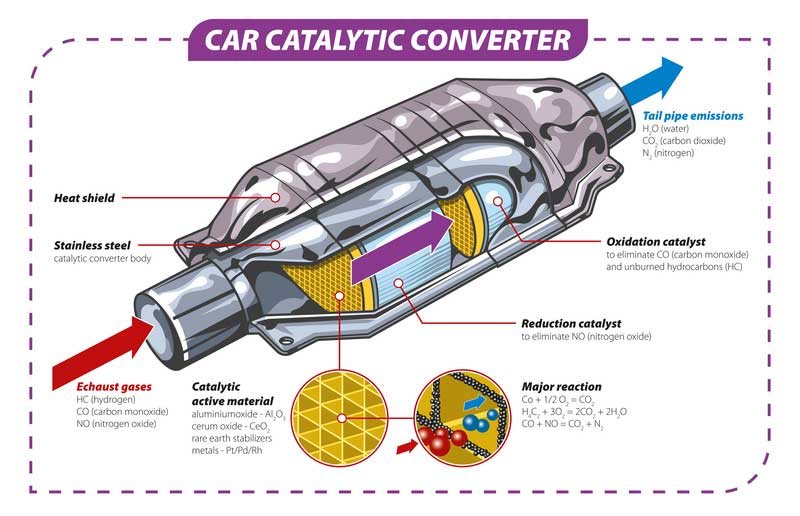
Rhodium is found in the honeycomb part of the converter, and you can easily recover the metal through a recycling process. Rhodium found in the catalytic converters does not lose its properties, and you would be safe recycling it.

Rhodium is least likely to be affected by air, water, and acids. Thus the acidic toxins produced alongside the exhaust fumes will not make the metal lose its properties.
The metal produces acetic acid through catalytic carboxylation, which is the synthesis of carbonyl compounds. Thus, it is a sturdy metal that rarely loses its properties.
The recycling company should have the latest technology systems and be energy-efficient. Moreover, it should have an effective waste system that reduces environmental pollution at the expense of the metal.
What Cars Have Very Expensive Catalytic Converters?
Ferrari F430 has the most expensive catalytic converter because it has two converters. Ford Mustang, Ford F-250, Ram 2500, and Lamborghini have relatively expensive catalytic converters.
These cars have larger engines thus would need larger or additional catalytic converters. Thus if a car needs two converters, it means it would need more rhodium metals. Moreover, larger catalytic converters would need more rhodium to cleanse the fumes effectively.
Where Does Rhodium Come From?
Rhodium is a rare non-reactive metal discovered by William Wollaston in 1803 and is obtained as a by-product of nickel and copper refining.
What Kind Of Metal Is Rhodium?
Rhodium belongs to the platinum metals of periods 5 and 6 and group 8 on the periodic table. Mostly the metal is used as an alloy that hardens platinum.
This precious silver-white metal is highly reflective and non-reactive, and corrosion-resistant. It can give jewelry an attractive finish and will be used to produce reflective surfaces for optical instruments.
Combined with rhodium, platinum becomes hard and loses weight at high temperatures more slowly than the pure metal. The alloys would be used to create furnace crucibles, catalysts in hot chemical environments, and spark-plug electrodes. The alloy is also useful for nitric acid manufacture as it withstands acids and high temperatures more.
Where Is Rhodium Found?
The metal is the rarest of the platinum group and, if often found, platinum mining mostly in South America, South Africa, Russia, and copper-nickel ores in Canada.
Why Does Rhodium Become So Expensive?
Rhodium cleans fumes from car exhaust, and thus its demand has increased due to emission restrictions. It faces a supply deficit due to the growing demand from the automotive sector to meet the stringent emission norms.
Thus the low supply has made its price double and is now costlier than gold. An ounce of rhodium costs more than cars like Tata Harrier, Toyota Innova, and Kia Carnival. This supply issue has led to rhodium catalytic theft in the US due to phenomenal price movement.
The closing of the South African mines has contributed to the metal price as the country had been the largest rhodium producer. The supply shortage due to plunging metal mines has affected the rhodium price.
Moreover, the suppliers are releasing little rhodium into the market, which creates a supply shortage, increasing the price of the goods.
The corona pandemic has affected the mining sector, and there has been investment in the mines during the period. South Africa was the worst hit, and some of the underground mines are yet to be fully functional.
Car manufacturers want more rhodium metal in Europe, China, and the US to meet the stringent norms to maintain clean air. The high demand impacts the metal price, and most car manufacturers would use the metal to clean the exhaust fumes as it is very resistant to corrosion.
Moreover, it uses other industries due to its chemical and physical properties, which adds to its demand.
Rhodium is hard to extract from the core, and the scarcity continues to impact its prices. Its price fluctuates at high levels, and the volatility might be a norm. Thus, the projected prices might make supplies keep the metal off the market, creating a deficit and more price increases.
What Is The Price Of Rhodium Today?
Pure rhodium goes for $290 per gram, but the price would depend on the metal quality to be more or less than this. You can act as a middle person by buying the metal from the mines and selling it to car manufacturers at a high price.
Rhodium might have more value in the future due to supply and demand issues, and thus buying and reselling the metal would be a good business.
However, if you want to sell an old catalytic converter, it might be worth $399 to $1500 at the local wrecking store. The high prices can be attributed to other highly valuable metals like palladium. However, you can set up a recycling company that can separate the metals from the catalytic converter fetching high prices.
Conclusion
Strict car manufacturing regulations require high-quality catalytic converters which filter out carbon dioxides and other toxins which affect the environment.
However, the demand for this rare metal has made its price go high. At the moment, pure rhodium goes for $290 per gram. The metal’s supply has been impacted by the high demand from the car manufactures, declined mining due to coronavirus pandemic, and distortion in the supply chain.
